50-30-20 Budgeting strategy
Having a budget can help you stay on top of bills, pay off debt and save for long or short-term goals. There are many ways to go about it.
One budgeting strategy is the 50/30/20 approach, which requires you to designate a portion of your earnings to three categories.
Some of the benefits include being able to manage your money without making too many sacrifices. It’s also simple to follow in comparison to some of the other budgeting strategies.
In this article we look at how it works and some areas to consider.
How does the 50/30/20 budgeting strategy work?
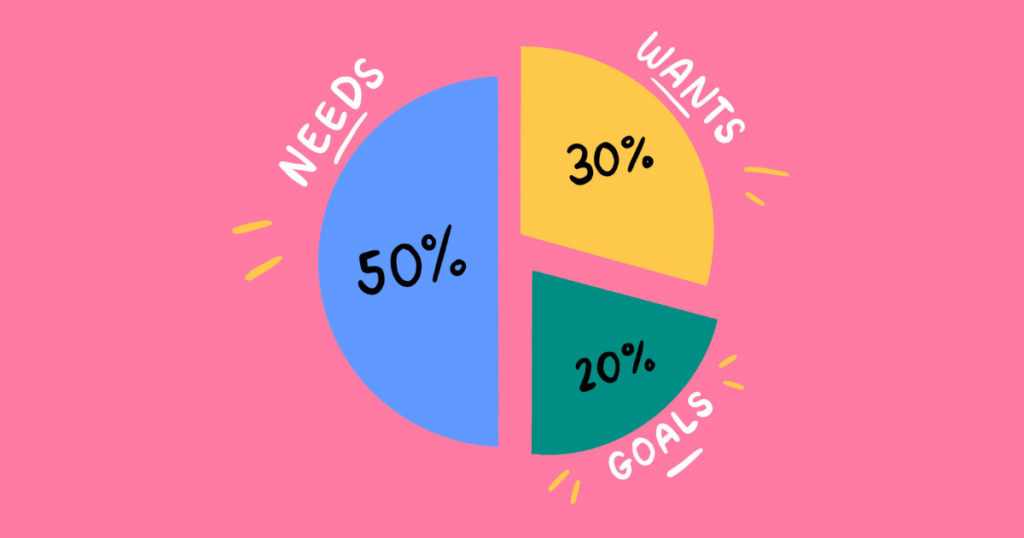
The 50/30/20 budgeting strategy helps you to divvy up your take-home pay into three main areas – needs, wants and savings, so you can make sure you’re allocating money to the things you need and want while also making progress towards your savings goals.
50% to your needs
This is where you allocate half of your take home pay (this is your income after tax) to essential living expenses – things that you can’t live without. This could include:
- rent or mortgage
- basic food needs
- utilities – electricity, gas, phone bills
- insurance and medical
- personal loans/credit card repayments
- transport payments – car registration/public transport
- family costs – childcare, school fees.
30% to your wants
30% of your take home pay can be allocated to things that you enjoy but you don’t need to survive. This may include:
- subscriptions/memberships – gym, Netflix
- luxury food expenses – eating out, takeaway, alcohol
- retail purchases
- gifts
- entertainment – concert tickets, weekends away.
20% to your savings or debt
Your final 20% is then allocated to financial goals that you need to save for. This could include a home deposit or investing in the share market.
If however, you have high-interest debts such as a personal loan or credit card bill, you may want to consider paying these off first before adding any money into savings. This is because the interest rate on loans is higher than the interest you’ll earn by keeping your savings in a bank.
Putting the 50/30/20 budgeting strategy into practice
If your fortnightly take home pay was $4,000 a month, half of it ($2,000) would be set aside for all your needs including bills and rent/mortgage. $1,200 would go towards social outings and entertainment, and $800 would be allocated to a long-term savings goal like a home deposit.
How to create a budget using the 50/30/20 strategy
Creating a budget based on the 50/30/20 strategy requires you to look at your income, assess your current spending habits, set goals and then readjust your budget regularly. Here’s how to get started.
Step 1: Determine your income
The first step to creating a 50/30/20 budget is to determine your after-tax income – how much money you bring home after paying tax. This will give you a realistic view of how much money you have available.
You want to include all income sources like your salary, investments, pension or government benefits. If you work in a traditional job, your payslips are a good starting point. If you don’t have a regular income, you can work out the average amount you would normally be paid per month.
Step 2: Assess your current spending
Next, it’s time to understand your spending habits including how much you spend on what and evaluate how this fits into the 50/30/20 method.
Review your expenses from the prior month then categorise each expense into one of the three categories – needs, wants and savings/debt.
Once you’ve added up the last month’s expenses, you can determine how much of your income is going into each category, and most importantly, whether your current spending complies with the 50/30/20 rule. If not, you’ll need to make adjustments.
It’s important to note that this budgeting approach may not work for everyone, particularly those on a low income with high living expenses.
Step 3: Make a plan
If your current spending habits and expenses don’t quite align with the 50/30/20 rule, you’ll need to make some changes. This might include reducing your spending on ‘wants’ or finding places to cut back on your ‘needs’.
The good news is there are many ways you can do this. Here’s some examples:
- Shop around for better deals on your home loan, electricity and insurance by researching the market. This can end up saving you hundreds of dollars over the long term.
- Cut down on subscriptions or memberships you don’t use. Make sure you’re getting all the concessions you’re entitled to such as rebates and discounts.
- Check out government and council rebates to reduce your energy bill and consider switching to energy efficient lightbulbs.
- Reduce grocery spending: meal planning is a simple way to reduce wasting food. Finding recipes that use the same ingredients means you’re more likely to use up an entire bag of vegetables.
- Reduce spending on takeaways or eating out by trying a new recipe at home. Remember that even small savings can add up to a lot of money over time so it’s worth making changes and searching for better deals.
Step 4: Pay off any high-interest debt
Now that you’ve set yourself a goal and made changes to your spending to achieve it, you’ll hopefully be saving at about 20% of your income. But before you start putting this into savings, considering paying off any high-interest debts first if you have them.
High-interest debts include personal loans or credit card bills that attract a high interest rate on your loan amount. Things like your HECS student loan or your home loan aren’t included here, as these attract a much lower interest rate. Once your high-interest debt is gone, this portion of your income can then be dedicated to savings.
Step 5: Reassess regularly
Once you’ve set up your budgeting strategy, it’s important to categorise your expenses every month to ensure you’re still in line with your 50/30/20 goals. As you become more familiar and comfortable with your budget, you can check it less frequently.
Is the 50/30/20 rule right for you?
The good thing with this budgeting strategy is you can use the percentages as a guide and change them depending on your situation.
For example, if you’re earning a low income but you have high living expenses, such as if you’re living in a major city, your essential expenses might be more than 50% of your income so you may need to adjust the percentages.
While this approach may be a good starting point for beginners, it’s not for everyone. Consider consulting a financial coach if you need help choosing the right budgeting strategy or you.
Source: MLC



